New Look, Same Limitations: Intune’s Company Portal Facelift
September 30, 2024UncategorizedIntune,Company Portal
Microsoft recently gave the Intune Company Portal app for Windows a visual refresh, but while the UI improvements are nice, they don’t solve some of the more pressing issues. If you were hoping for new functionality to make life easier for IT admins, you might be left wanting more. The updated design feels more modern and polished, but the lack of deeper functional updates leaves a few gaps—like the missing "retry" button for required apps and the absence of a quick way to gather logs.
What’s Changed?
The new design for the Company Portal app focuses on improving the user experience through a cleaner interface.
Here’s what’s new:
- Updated Navigation: The navigation pane has been redesigned for easier access to apps, devices, and account settings. It’s sleeker and more intuitive, but the functionality remains largely the same.
- Enhanced Visuals for App Details: App descriptions, version numbers, and installation status are now presented more clearly, offering better readability and a more organized layout.
- UI Consistency Across Platforms: The updated Windows version now aligns more closely with the Company Portal app experience on iOS, Android, and macOS, creating a more unified look across platforms.
What’s Missing?
While the visual overhaul is appreciated, some important features are still absent:
- No "Retry" Button for Required Apps: For IT admins managing required apps, the lack of a "retry" option remains a frustrating oversight. If an app fails to install the first time around, users are left in a bit of a limbo, having to wait for another automatic attempt. A manual "retry" button would provide much-needed control in these situations.
- No Quick Way to Gather Logs: The updated interface still doesn’t include a fast, user-friendly way to collect logs for troubleshooting. Gathering logs is a crucial step for IT teams when diagnosing issues, and a quick method to do this directly within the Company Portal would save significant time and effort, especially when resolving support tickets.
- Better Application detection: If you've ever tried uninstalling an app through the Company Portal, you've probably encountered the issue where the uninstall button doesn’t show up right away or an app that has already been isntalled, has not been detected.It would be great to see improvements with detecting app statuses in real-time. While a fresh look is great, fixing these basic functionality issues would have been a much more impactful update.
Why This Matters
The updates to the Company Portal make the app look better, but for IT admins and organizations managing large device fleets, the functionality is what really matters. Without the ability to easily retry failed app installations or collect logs, the frustrations of managing devices remain.
Sure, the cleaner UI is a welcome change, but it’s the absence of deeper tools—like better error handling for app installs and streamlined troubleshooting—that keeps this update from being as impactful as it could be.
Wrapping It Up
Microsoft’s redesign of the Intune Company Portal app feels like a step in the right direction, but it’s mostly about looks. The missing "retry" button for required apps and the lack of a quick way to gather logs are still glaring omissions that make device management harder than it needs to be.
So while the fresh look is nice, it’s still a case of form over function. Hopefully, future updates will bring the essential tools that admins and users need to make their lives easier. Until then, it’s all about appreciating the superficial improvements while managing the same old challenges.
Microsoft's OOBE Update Snafu: The Rollback We Didn’t See Coming
If there’s one thing we can always count on with technology, it’s that updates have a knack for showing up at the most inconvenient times. Recently, Microsoft made a bold move by deciding to push updates during the Out-of-Box Experience (OOBE)—yes, right as you’re setting up that fresh new device. The idea was simple: deliver the latest updates immediately, ensuring users start off on the most secure and current version of Windows. But as many quickly found out, not everyone was thrilled to have their setup interrupted by an unexpected downloading marathon.
The Plan: Updates, Right from the Start
When Microsoft announced this change, the logic made sense: if users could get the latest patches and security fixes as part of the OOBE, they’d start off on the right foot, avoiding the dreaded post-setup update cycle. In theory, it seemed like a smart move—why not handle everything in one go?
But in practice, it created frustration. Imagine being all set to start using your new device, only to be delayed by a long update process. For businesses, where efficiency is key, this approach turned into a time-sink.
The U-Turn: Backpedaling on the Rollout
And then came the backtrack. It seems Microsoft heard the collective groans loud and clear. After initially doubling down on pushing updates during OOBE, the tech giant quickly adjusted its approach. Microsoft pulled back on making updates mandatory during the initial setup, giving users the flexibility to defer them until a more convenient time.
Why the Shift?
So, what prompted the change of heart? It likely came down to a mix of user feedback and real-world issues. Businesses, in particular, found the enforced update process disruptive—especially when trying to roll out large numbers of devices efficiently. Plus, having devices sit through extended update periods during the first-time setup was a bit like forcing everyone to wait at the starting line before the race could even begin.
Why This is a Big Deal for Enterprises
This wasn’t just a minor inconvenience—it was a major headache for enterprises. Large organizations often need to deploy hundreds or even thousands of devices at a time. During these mass rollouts, speed and efficiency are crucial. Imagine an IT department trying to get a fleet of new laptops ready for use, only to have each one bogged down by an unexpected update marathon during the initial setup process. For enterprises, control over when and how devices are updated is critical. IT teams want the flexibility to decide when updates are applied, allowing them to test updates properly before pushing them out across an entire fleet. The ability to block updates, particularly if there are concerns about compatibility or conflicts with existing applications, is vital for ensuring smooth operations.
Microsoft’s original OOBE update strategy took this control away, forcing businesses to either wait for updates to complete or risk introducing untested changes into their environment.
The backtrack by Microsoft now ensures that enterprises can maintain their customized update schedules, test thoroughly, and block problematic updates until they’re fully vetted—avoiding the chaos that can come from unplanned downtime.
Moving Forward: Balancing Updates and Usability
The whole ordeal highlights a delicate balance that software companies like Microsoft have to strike. On one hand, it’s crucial to keep devices secure and up-to-date from the moment they’re powered on. On the other, users—especially businesses—want control over when those updates happen, particularly in critical environments where time is of the essence.
For now, it looks like Microsoft has learned a valuable lesson about when to push those updates—and it’s a good reminder that even in the tech world, timing is everything. The concept of updating at the start isn't a bad one, it just needs to be done in a way the enterprise can controll the behaviour!
WSUS is Out—What’s Next? Microsoft’s Shift to Modern Update Management
September 23, 2024BlogIntune,WSUS
WSUS, the trusty tool many of us have relied on for patch management, is officially heading for the exit. https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/windows-it-pro-blog/windows-server-update-services-wsus-deprecation/ba-p/4250436
With Microsoft’s announcement of WSUS deprecation, the question looms: “What’s next for update management?” Don’t worry—there’s a cloud-friendly future waiting. Let’s break down what this means, when it’s happening, and how you can stay ahead of the curve.
Why is WSUS Being Deprecated?
After more than two decades of faithfully distributing patches, WSUS is finally being phased out. The tool was a staple in on-premises environments, offering IT admins granular control over which updates were deployed and when. However, with the shift to cloud-based infrastructures, Microsoft is steering towards more modern, scalable, and flexible solutions.
Simply put, WSUS is being retired because it wasn’t designed for today’s hybrid and cloud-first environments. The modern workplace demands seamless updates across diverse device fleets, from on-prem servers to remote laptops. Enter Microsoft Endpoint Manager, Intune, and Windows Update for Business, the cloud-driven solutions poised to take over WSUS’s role.
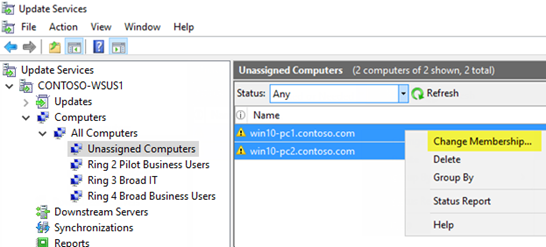
When Will WSUS Be Deprecated?
Microsoft has outlined a gradual deprecation process, which means you won’t wake up tomorrow to find WSUS suddenly gone. Instead, the timeline allows for a smooth transition:
•Active Deprecation: With each new release of Windows Server, you’ll see more features of WSUS being retired.
•Support Ends with Server 2025: Official support for WSUS is set to end by 2025, giving organizations time to transition.
This gives IT pros plenty of runway to adjust their update strategies. However, it’s best not to wait until the last minute to explore alternatives.
What’s Next? The Modern Alternatives
Now that WSUS is heading into the sunset or bin, Microsoft has made it clear where the future lies—Microsoft Intune. This cloud-based platform, combined with Windows Update for Business, is your ticket to managing updates across hybrid environments.
•Microsoft Intune: As part of Microsoft Endpoint Manager, Intune lets you manage updates and policies from a central hub, whether devices are on-premises or remote. The flexibility to manage Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android from a single console is a game-changer.
•Windows Update for Business (WUfB): Integrated within Intune, WUfB allows you to automate update deployment directly from Microsoft’s cloud services. It offers more streamlined management of Windows updates without the need for the infrastructure WSUS required. Plus, WUfB is built for the modern era—it scales as your device fleet grows and adapts to the needs of a hybrid workforce.
Granularity: WSUS vs. WUfB
One thing to note is that WUfB is less granular compared to WSUS. With WSUS, admins had precise control over individual updates, allowing them to pick and choose which patches were deployed and when. In contrast, WUfB embraces an “evergreen” approach, which focuses on keeping devices automatically updated with the latest features and security patches. While this ensures devices stay current and secure, it offers less flexibility for those who prefer to selectively approve updates or hold back specific upgrades. However, for many organisation, the benefits of an evergreen environment far outweigh the need for micromanaging individual updates. Let's face it, the evergreen approach is here to stay.
If your organisation requires more granular control over updates—similar to what WSUS provided—then third-party patch management tools may be the way to go. While Windows Update for Business (WUfB) offers a more streamlined, cloud-friendly approach, it lacks the ability to pick and choose individual updates with the same level of detail. For businesses that need to carefully manage which patches are deployed or need to hold back specific updates for testing, third-party tools offer the flexibility and granular control that WUfB doesn’t. These tools can handle Windows updates, as well as patches for third-party applications, giving you a more tailored approach to update management without sacrificing control, however this needs to be balanced against the cost of essentially paying twice for the same service.
How to Prepare for the WSUS Transition
Transitioning away from WSUS may seem daunting, but here are a few steps to make the process smoother:
1. Audit Your Current Setup: Start by taking stock of your WSUS deployment and assess how it fits into your broader IT strategy.
2. Evaluate Microsoft Intune: If you’re not already using Intune, this is the perfect time to explore how it can streamline your device management and update strategy.
3. Plan for Migration: Create a roadmap for migrating from WSUS to Intune, ensuring you have the resources and time to test, train, and fully transition your IT team.
The Future is Cloudy (and That’s a Good Thing)
While WSUS has been a reliable workhorse, the future of IT update management is all about the cloud. With Intune and Windows Update for Business, you’ll have the flexibility, scalability, and security needed to thrive in a modern, hybrid world. So, wave goodbye to WSUS and say hello to a more agile, efficient way of managing updates.
SCCM’s Long, Slow Death: Why Intune is Dancing on its Grave
System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) has served IT teams for years, but its slow death is undeniable as Microsoft pivots toward Intune and cloud-first solutions. The shift reflects the changing needs of modern IT environments, driven by mobility, remote work, and cloud-based services. Let’s dive deeper into why SCCM’s days are numbered and what you can expect as it fades into the background.
1. Legacy Infrastructure Doesn’t Cut It Anymore
SCCM was a powerhouse in its prime, built for a time when most IT operations were centralized and on-premises. Enterprises relied on SCCM’s complex infrastructure, including SQL databases, distribution points, and local servers to deploy updates and applications. Back then, it made perfect sense—but in today’s cloud-driven world, these requirements are cumbersome. IT teams now prefer lightweight solutions that don’t require large on-prem servers and heavy management infrastructure.
SCCM's reliance on physical infrastructure makes it difficult for IT teams to manage today’s distributed, hybrid workforce, where devices are scattered across multiple locations. Intune’s cloud-first model, on the other hand, allows IT admins to manage devices from anywhere, without the need for physical servers.
With remote work here to stay, relying on SCCM feels like dragging along an anchor in an era of lightweight speedboats. Microsoft’s focus is increasingly on Microsoft Endpoint Manager and Intune, leaving SCCM to manage its decline while businesses adopt cloud solutions.
2. SCCM’s Bloated Costs and Complexity
SCCM’s infrastructure is not only heavy but also costly. From maintaining on-premises servers to ensuring databases are up to date, SCCM requires significant financial and human resources to run effectively. IT admins need to constantly monitor infrastructure, manage backups, update software, and troubleshoot issues. In contrast, Intune’s cloud-native design allows organizations to offload infrastructure management to Microsoft, drastically reducing costs and administrative burden.
Intune’s approach is far simpler. Updates are managed automatically in the cloud, reducing manual maintenance tasks and freeing up time for IT teams to focus on more strategic projects. Companies no longer have to worry about distribution points, patch management, or managing complex environments, as all of this is taken care of through Intune’s cloud service.
The Forrester Total Economic Impact (TEI) study on Intune shows that organizations switching from SCCM to Intune report up to 60% reduction in infrastructure costs, making it clear that sticking with SCCM is not just outdated, but financially inefficient.
3. Sluggish Updates and Innovation
SCCM is still receiving updates, but it’s clear that these are mostly maintenance updates rather than innovations. Microsoft’s strategic investment is going into Intune and its integration with Azure, Microsoft 365, and Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) features. SCCM’s development is noticeably slower, and the latest features are almost exclusively appearing in Intune.
For example, SCCM’s Windows Update management requires manual configurations and often takes longer to execute, whereas Intune offers Windows Update for Business or Autopatch, a cloud-based update management tool that streamlines the entire process. Intune can push updates to remote devices without the need for cumbersome VPNs or relying on devices being connected to the corporate network.
Intune’s roadmap is full of new features aimed at streamlining remote work, improving security, and automating device provisioning—all areas where SCCM struggles to keep up.
4. Deprecation of Key SCCM Features
Microsoft’s gradual deprecation of SCCM features is perhaps the clearest indicator of SCCM’s future. Legacy Reporting, for instance, has been replaced by Intune’s cloud-based analytics which offer more powerful insights without the infrastructure burden. App deployment, once a strong point of SCCM, has also been overtaken by Intune’s intuitive and cross-platform management capabilities.
As Microsoft continues to retire these core SCCM features, organizations relying heavily on SCCM are finding themselves at a crossroads. The writing is on the wall—while SCCM may still function, it’s on life support. Intune’s app management, with its ability to handle Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android devices seamlessly, has made SCCM’s application deployment process look antiquated.
5. Co-Management: The Transition Bridge
For organizations not ready to cut ties with SCCM entirely, Microsoft offers a co-management model that allows businesses to use both SCCM and Intune during the transition period. With co-management, IT teams can move workloads such as compliance policies, device configuration, and security management to Intune while continuing to use SCCM for legacy tasks.
Co-management offers a softer landing for companies transitioning from SCCM to Intune, but make no mistake—it’s still a transition, not a long-term solution. As SCCM continues to lose features and Intune gains new capabilities, the balance will inevitably tip towards full migration.
6. The Future is Cloud-Based
Ultimately, SCCM’s demise is part of the broader trend of IT moving to the cloud. The advantages of cloud-based solutions like Intune are undeniable—reduced costs, simplified management, scalability, and the ability to handle the remote work environments that define the modern workplace. The long, slow death of SCCM is just another step in this ongoing shift.
Microsoft is clearly placing its bets on Intune and the Microsoft Endpoint Manager ecosystem, and businesses that are still clinging to SCCM are running out of time. Planning for the future means planning for a world where cloud-based management is the norm, and SCCM is nothing more than a chapter in IT history.
Windows Enrollment Just Got a Glow-Up: Here’s the Good, the Bad, and the Patchy
September 17, 2024BlogIntune,Autopilot,Updates
Starting October 2024, new Windows 11 devices (version 22H2+) will automatically download and install quality updates during the Out-of-Box Experience (OOBE) when enrolled via MDM like Intune. This ensures devices are secure before user login.
Advantages:
- Better Security: Immediate patching reduces risks from out-of-date software.
- Compliance: Ensures policies are met from day one.
Disadvantages:
- Longer Enrollment: Updates during OOBE might delay device handoff.
- Access Pass Adjustments: Temporary Access Passes may expire before setup is complete.
- Updates whether you want them or not: No more choice in the process.
Final Thoughts:
While the enhanced security is a significant benefit, the extended setup time could become a challenge for organizations with tight provisioning schedules. Admins managing large fleets may need to plan for the additional time required for these updates. The Temporary Access Pass issue also means careful coordination will be needed, particularly in environments relying on quick deployments or where devices are being "White Gloved" on behalf of Assistive Technology users.
For businesses prioritizing immediate security and compliance, this update is a step in the right direction. However, organizations focused on speed or with existing streamlined processes may face slight disruptions. Balancing security with efficiency will be key. One thing is for sure, Microsoft is keen for you to be on the latest updates!
Autopilot 2.0: Microsoft’s Slick New Rollout for Gov & Enterprise!
June 7, 2024BlogIntune,Autopilot
Microsoft has dropped a fresh upgrade for Windows Autopilot, and it's a game changer, especially for IT admins in government and large enterprises. The new features streamline the onboarding process, improve error handling, and provide support for government clouds like GCC High and DoD. If you're dealing with large-scale deployments, this update just made things smoother and less of a headache.
Key Features You’ll Love:
- Improved Out-of-Box Experience (OOBE): You can now see real-time progress as devices are onboarded. This not only gives you peace of mind but also lets you track issues before users get their hands on the device. The new UI is cleaner and provides more insight into the deployment process, which helps IT teams pinpoint problems quickly.
- Stronger Error Handling: The update includes enhanced error resiliency, meaning that even if something goes wrong during the setup, the system can handle it better, reducing the number of failed deployments. This saves time and frustration, especially in large environments where downtime can be costly.
- Government Cloud Support: For those managing sensitive environments, Autopilot now has extended support for government clouds, including GCC High and DoD. This means that government institutions with high security requirements can now enjoy the benefits of Autopilot without compromising on compliance or control.
 Why It Matters:
Why It Matters:
The latest Autopilot updates are tailored for large-scale deployments, making it easier to manage thousands of devices while ensuring they stay secure and up-to-date. With better visibility into the onboarding process and a stronger focus on error resilience, IT departments can spend less time troubleshooting and more time focusing on strategic tasks.
For government bodies and enterprises that require strict security and compliance, these features are a blessing. The ability to deploy devices into secure environments like GCC High and DoD clouds without extra steps means faster, more efficient rollouts.
What’s the Catch?
While the updates bring a lot of improvements, it’s worth noting that device setup may still take some time, especially with larger batches. But overall, these enhancements mean fewer bumps along the way, less downtime, and a more intuitive deployment process.
Final Thoughts:
This Autopilot update is all about saving time, reducing errors, and providing greater control for IT admins working with large or highly secure environments. If you’re an IT admin in government or enterprise, these changes are worth exploring. Not only will they improve how you manage devices, but they’ll also give you more confidence in the deployment process from start to finish.
For more details, check out the full announcement here.
Welcome
Welcome everyone to the first blog of modern-managed.com! This site has been a long time in the making, having purchased the domain over a year ago, I finally decided that I needed to sit down and write some content for it.
This site will replicate some of the work I did on my own company Cloudable in the blog section, but I wanted to separate out the blog from my commercial consultancy.
Over the coming weeks, months and years, I plan to add lots of helpful content from some co-workers and I that you will hopefully find useful. I will also import all the old articles from the cloudable blog.
Intune Autopilot – Part 2 – Moving in the right direction!
March 3, 2020Intune,Autopilot,shared devicesGuide
Cont.
So if you've read part one, then you're looking for a way to set up an Intune managed Autopilot device to be shared among multiple users.
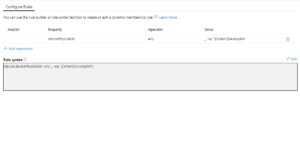
The chances are that you're already using autopilot for your single-user devices. Which means that you already have an Azure AD Dynamic Group, probably using a dynamic query such as:
(device.devicePhysicalIDs -any (_ -contains "[ZTDId]"))
The problem with this approach is that it's going to lump all of our autopilot devices into one AAD Dynamic group, which is no good if we need multiple deployment profiles (User Driven + Self-Deploying profiles). So we need a way to separate these devices. Enter the OrderID field...
The OrderID field, also referred to as GroupTag will allow us to create different groups of Autopilot devices, so that we can deploy Single User laptops, Shared PCs, and Kiosk devices all with different profiles and policy sets. However, if we are using the ZTDId tag, the chances are that none of our existing computers has the order IT field populated.
Therefore we need to populate the OrderID value for all existing devices and change our Dynamic AD groups to match the OrderID, not all autopilot devices.
Thankfully, Nicola Suter has come to the rescue here. He has written a PowerShell script that will connect to Graph API, and allow us to change the OrderID field in bulk. https://tech.nicolonsky.ch/bulk-update-windows-autopilot/ In this example. I'm going to use a group tag of "autopilot" to signify a standard user-driven deployed device, therefore we will use Nicola's scripts to change the group tag to "Autopilot" on all existing devices.
In conjunction, with this, we also need to change the Dynamic group query in Azure AD from targeting ZTDid to something like this:
(device.devicePhysicalIds -any _ -eq “[OrderID]:Value”)
Where "Value" is the value, you want to put in the OrderID field.
Once we have done this, we can start building a new policy and profile set for our other devices. In part 3, we will explore a multi-user desktop and kiosk mode deployment alongside traditional user-driven deployments.
Intune Autopilot - Sharing the love - Part 1
January 27, 2020Intune,AutopilotGuide
Over the last 18 months, I've had great success deploying modern-managed devices for clients, using a mix of Azure Active Directory, Intune and Autopilot. Autopilot has always worked great in scenarios where one user = one workstation, but what about a replacement for that traditional domain-joined PC which you would deploy for shift workers or in multi-user situations where one computer = 5 users?
There are a few ways that I have found a multi-user device can be set-up, but these all have drawbacks.
Build a PC then AAD join it:
On the face of it, this seems like the most straightforward option. The PC can be AAD joined and added into AAD Device groups to receive policies. However, the drawback with this approach is that the machine will be listed in AAD as a device under the user that AAD joined it. This can lead to admin accounts with tens of devices listed under them and a potential requirement to lift the "per user device limit" within AAD.
It's also a royal pain in the backside to have to assign group memberships manually, and policy application appears to be a little spotty the moment you transition to a standard user.
SharedPC CSP
Microsoft has thought of this and created a SharedPC CSP policy. SharedPC CSP comes with several advantages such as Guest account Management, Local Storage Policies, Power Policies, Fast first sign-in and Education Policies, all of which make management and sign-in much easier. But for me, this CSP has one critical flaw - it disables the OneDrive client completely!!
If like me, you've been encouraging people to take advantage included 1TB OneDrive space per user in Office 365, then you've probably migrated users' documents to OneDrive and are using policies such as KFM (known folder move). OneDrive client is critical to a Shared PC; otherwise, users will are forced to use OneDrive online to access their documents. It also gives no easy way to roam documents between shared PCs, for example at a reception desk with two seats.

So, how do we deploy an Intune Autopilot device for multiple users with all of our usual Line of Business apps?
The answer is Intune Self-Deploying Mode but without SharedPC CSP!!
What, I hear you cry, that sounds counter-intuitive, but it works. We'll let the self-deploying mode take care of our AAD join and then layer some custom Policies on top to cover the other bits.
The self-deploying mode requires adding another Autopilot deployment profile, which means you must make some changes to your existing autopilot configuration. In Part 2, I'll go into the changes that you need to make to prepare your environment for multiple deployment profiles.
Is ADFS now dead?
For those of you keeping an eager eye on cybersecurity, NCSE published some new guidance for securing Office 365 earlier this year. This new guidance includes one significant change from Microsoft, which some may find a little controversial.
Microsoft now recommends that hybrid environments – i.e. those that use Active Directory Domain Services and Azure AD – should prefer native authentication against Azure AD rather than ADFS.
In Microsoft-speak this is ‘Seamless SSO with Password Hash Sync’, configured to use either per-user or Conditional Access MFA.
Password synchronisation with the cloud can feel like a scary thing to do, but in actuality, organisations using Azure AD as their primary authentication source will lower their risk compared with ADFS.
This is because:
- It’s the hashes of your password hashes that are sent to Azure AD, and not the reusable NTLM hashes commonly discussed in “pass the hash” attacks. This means that the credentials sent to Azure AD can’t be used to authenticate to any of your on-premise infrastructures that rely on Active Directory.
- We are already relying on Azure AD to make access control decisions regulating who can see which data, hosted in Office 365. So we already need to trust that it’s built and operated securely. Storing password hashes doesn’t change that security requirement.
- The availability of Office 365 will no longer be affected by any outages or downtime suffered by your on-premise ADFS or Active Directory infrastructure.
For those interested, the new Microsoft guidance can be found here: It’s a brave new world out there!